D.2 Programs for second-order analysis
Program D.14 (yspESTframe2LaheWFI.m)
D.159 ![[*]](./icons/crossref.png) -
is used to compute the displacements and forces of a plane frame.
-
is used to compute the displacements and forces of a plane frame.
Called function:
-
- - Lahe2FrameDFIm.m.
Function D.40
(Lahe2FrameDFIm(baasi0,Ntoerkts,esQkoormus,esFjoud,
sSolmF,tsolm,tSiire,krdn,selem)) D.160 ![[*]](./icons/crossref.png) ,
, ![[*]](./icons/crossref.png) ,
, ![[*]](./icons/crossref.png) ,
, ![[*]](./icons/crossref.png) ,
, ![[*]](./icons/crossref.png) - is used to assemble and solve the boundary problem equations for a plane frame.
- is used to assemble and solve the boundary problem equations for a plane frame.
Called functions:
-
- -
VardaPikkus(NSARV,NEARV,krdn,selem) D.161;
- -
ysplvfmhvII(baasi0,S,x,l,EA,GAr,EJ) D.162;
- -
ysplfmhvII(baasi0,S,x,l,EA,GAr,EJ) D.163;
- -
tnnusarv(l1,s1,ea1) D.164;
- -
ysplfhlin(baasi0,x,EA,GAr,EJ)) D.165;
- -
ylqvII(baasi0,S,x,lp,qz,EA,EJ) D.166;
- -
yzhqz(baasi0,x,qx,qz,EA,EJ) D.167;
- -
ylfhvzII(baasi0,S,x,l,a,Fz,EJ) D.168;
- -
yzfzv(baasi0,x,a,Fx,Fz,EA,EJ) D.169;
- -
VardadSolmes(NSARV,NEARV,Solm,AB,ABB) D.170;
- -
SpTeisendusMaatriks(NSARV,NEARV,VarrasN,krdn,selem) D.171;
- -
SpTeisendusMaatriks2x2(NSARV,NEARV,VarrasN,krdn,selem) D.172;
- -
SpTeisendusUhikMaatriks2x2(VarrasN) D.173;
- -
SpTeisendusUhikMaatriks(VarrasN) D.174;
- -
SpTeisendusUhikMaatriks0x1v(VarrasN) D.175;
- -
SpToeSiirdeUvektor(NSARV,NEARV,VarrasN,krdn,selem) D.176;
- -
SpToeSiirdeWvektor(NSARV,NEARV,VarrasN,krdn,selem) D.177;
- -
SpToeSiirdeFiVektor(VarrasN) D.178;
- -
ylfmhvII(baasi0,S,x,l,EA,GAr,EJ) D.179;
- -
ytransfp(S,l,EJ) D.180;
- -
spSisestaArv(spA,iv,jv,sv) D.181;
- -
spInsertBtoA(spA,IIv,IJv,spvF) D.182;
- -
InsertBtoA(A,I,J,IM,JN,B,M,N) D.183.
Program D.15 (yspESTframe1LaheWFI.m)
D.184 ![[*]](./icons/crossref.png) -
is used to compute the displacements and internal forces for a plane frame.
-
is used to compute the displacements and internal forces for a plane frame.
Called function:
- - Lahe2FrameDFIm.m.
Function D.41 (ylfmhvII(baasi0,S,x,l,EA,GAr,EJ))
D.185 ![[*]](./icons/crossref.png) ,
, ![[*]](./icons/crossref.png) - is used to compute the transfer
matrix for a frame (Sign Convention 2) in a second-order analysis. Here,
- is used to compute the transfer
matrix for a frame (Sign Convention 2) in a second-order analysis. Here,
EA - axial stiffness of the element,
GAr - shear stiffness of the element,
EJ - bending stiffness of the element,
l - length of the element,
baasi0 - scaling multiplier for the displacements (i = EJ/l),
S - axial force.
Called functions:
-
- -
tnnusarv(l1,s1,ea1) D.186;
- -
ylfhlin(baasi0,x,EA,GAr,EJ) D.187.
Function D.42 (ysplfmhvII(baasi0,S,x,l,EA,GAr,EJ))
D.188 ![[*]](./icons/crossref.png) - is used to compute the transfer matrix for a frame (Sign Convention 2) in a second-order analysis. Here,
- is used to compute the transfer matrix for a frame (Sign Convention 2) in a second-order analysis. Here,
is used to assemble and solve the boundary problem equations for a plane frame.
EA - axial stiffness of the element,
GAr - shear stiffness of the element,
EJ - bending stiffness of the element,
l - length of the element,
baasi0 - scaling multiplier for the displacements (i = EJ/l),
S - axial force.
Called functions:
-
- -
tnnusarv(l1,s1,ea1) D.189;
- -
ysplfhlin(baasi0,x,EA,GAr,EJ) D.190.
Function D.43 (ylfhvzII(baasi0,S,l,x,a,Fz,EJ))
D.191 ![[*]](./icons/crossref.png) ,
, ![[*]](./icons/crossref.png) - is used to compute the loading vector of a point load for a frame in a second-order analysis. Here,
- is used to compute the loading vector of a point load for a frame in a second-order analysis. Here,
Fz - point load acting in the z direction,
a - distance of a load point from a start point,
EJ - bending stiffness of the element,
l - length of the element,
baasi0 - scaling multiplier for the displacements (i = EJ/l),
S - axial force.
Called functions:
-
- -
tnnusarv(l1,s1,ea1) D.192;
- -
yzfzv(baasi0,x,a,Fx,Fz,EA,EJ) D.193.
Function D.44 (ylqvII(baasi0,S,x,lp,qz,EJ))
D.194 ![[*]](./icons/crossref.png) ,
, ![[*]](./icons/crossref.png) - is used to compute the loading vector of a uniformly distributed load for a frame in a second-order analysis. Here,
- is used to compute the loading vector of a uniformly distributed load for a frame in a second-order analysis. Here,
qz - uniformly distributed load along the z-axis,
EJ - bending stiffness of the element,
baasi0 - scaling multiplier for the displacements (i = EJ/l),
S - axial force.
Called functions:
-
- -
tnnusarv(l1,s1,ea1) D.195;
- -
yzhqz(baasi0,x,qx,qz,EA,EJ) D.196.
Function D.45 (ylfmII(S,x,l,EA,GAr,EJ))
D.197 ![[*]](./icons/crossref.png) ,
, ![[*]](./icons/crossref.png) - is used to compute the transfer matrix for a frame (Sign Convention 2) in a second-order analysis. Here,
- is used to compute the transfer matrix for a frame (Sign Convention 2) in a second-order analysis. Here,
EA - axial stiffness of the element,
GAr - shear stiffness of the element,
EJ - bending stiffness of the element,
S - axial force.
Called functions:
-
- -
tnnusarv(l1,s1,ea1) D.198;
- -
ylflin(x,EA,GAr,EJ) D.199.
Function D.46 (ylqII(S,x,l,qz,EJ))
D.200 ![[*]](./icons/crossref.png) - is used to compute the loading vector of a
uniformly distributed load in a second-order analysis. Here,
- is used to compute the loading vector of a
uniformly distributed load in a second-order analysis. Here,
qz - uniformly distributed load along the x-axis,
EJ - bending stiffness of the element,
l - length of the element,
S - axial force.
Called functions:
-
- -
tnnusarv(l1,s1,ea1) D.201;
- -
yzqz(x,q,EJ) D.202.
Function D.47 (ylffzII(S,l,x,a,Fz,EJ))
D.203 ![[*]](./icons/crossref.png) - is used to compute the loading vector for the point load in a second-order analysis. Here.
- is used to compute the loading vector for the point load in a second-order analysis. Here.
Fz - point load acting in the z direction,
a - distance of a load point from a start point,
EJ - bending stiffness of the element,
l - length of the element,
S - axial force.
Called functions:
-
- -
tnnusarv(l1,s1,ea1) D.204;
- -
yzfz(x,a,Fx,Fz,EA,EJ) D.205.
Function D.48 (ytransf(S,l,EJ))
D.206 ![[*]](./icons/crossref.png) - is used to compute a transformation matrix to transform the forces N and Q into the forces S and H in a second-order analysis. Here,
- is used to compute a transformation matrix to transform the forces N and Q into the forces S and H in a second-order analysis. Here,
EJ - bending stiffness of the element,
l - length of the element,
S - axial force.
Called function:
-
- -
tnnusarv(l1,s1,ea1) D.207.
Function D.49 (ytransfp(S,l,EJ))
D.208
![[*]](./icons/crossref.png) - is used to compute a transformation matrix to transform the forces S and H into the forces N and Q in a second-order analysis. Here,
- is used to compute a transformation matrix to transform the forces S and H into the forces N and Q in a second-order analysis. Here,
EJ - bending stiffness of the element,
l - length of the element,
S - axial force.
Called function:
-
- -
tnnusarv(l1,s1,ea1) D.209.
Function D.50 (ysplvfmhvII(baasi0,S,x,l,EA,GAr,EJ))
D.210 ![[*]](./icons/crossref.png) - is used to compute the sparse transfer matrix
(
- is used to compute the sparse transfer matrix
(
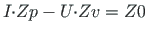 , Zp'=[Up Wp Fip Sp Hp Mp]) for a frame (Sign Convention 2) in a second-order analysis. Here,
, Zp'=[Up Wp Fip Sp Hp Mp]) for a frame (Sign Convention 2) in a second-order analysis. Here,
EA - axial stiffness of the element,
GAr - shear stiffness of the element,
EJ - bending stiffness of the element,
l - length of the element,
baasi0 - scaling multiplier for the displacements (i = EJ/l),
S - S - axial force.
Called functions:
-
- -
ysplfmhvII(baasi0,S,x,l,EA,GAr,EJ) D.211;
- -
spInsertBtoA(spA,IM,JN,spB) D.212.
andres
2014-09-09
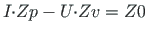 , Zp'=[Up Wp Fip Sp Hp Mp]) for a frame (Sign Convention 2) in a second-order analysis. Here,
, Zp'=[Up Wp Fip Sp Hp Mp]) for a frame (Sign Convention 2) in a second-order analysis. Here,