Next: 6.3 Illustrative frame problem Up: 6. The EST method Previous: 6.1 System equations for
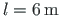 , carrying a uniform load
, carrying a uniform load
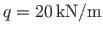 .
The
.
The
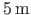 long column 3-4 and the
long column 3-4 and the
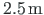 long column 2-3 are both loaded with a vertical force
long column 2-3 are both loaded with a vertical force
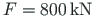 .
At node 2, a horizontal force
.
At node 2, a horizontal force
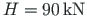 acts.
acts.
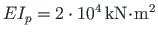 and that of the beam
and that of the beam
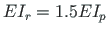 (
(
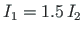 ); axial rigidity of the columns
); axial rigidity of the columns
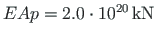 and that of the beam
and that of the beam
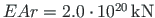 ; shear rigidity of the columns
; shear rigidity of the columns
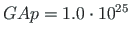 and that of the beam
and that of the beam
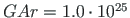 .
.
We wish to compute the displacements, reactions, internal forces, and draw the axial force, shear force and bending moment diagrams.
Problem Solving. To solve the problem, we use the EST method. The solving procedure includes the following.
epsdountil=0.0000001; # for iteration (max |S| increment) Number_of_frame_nodes=4 Number_of_elements=3 Number_of_support_reactions=5 spNNK=12*Number_of_elements+Number_of_support_reactions; Number_of_unknowns=spNNK Displacements and forces are calculated on parts ''Nmitmeks'' of the element Nmitmeks=4 # --- Element properties ---
EIp=20000; # kN/m^2 EIr=40000; # kN/m^2 # EAp=4.6*10^6; EAp=2.0^20; # EAp=4.6*10^6; EAr=6.8*10^20; # EAr=6.8*10^6; GAp=1.0e+25; GAr=1.0e+25; # GAp=0.4*EAp; # GAr=0.4*EAr;
baasi0=EIp/5 # scaling multiplier for displacements # baasi0=1.0; # Element load in local coordinates # qz qx qA qL # Uniformly distributed load in local coordinate z and x directions LoadsqONelement=4; esQkoormus=zeros(LoadsqONelement,4,ElementideArv);
baasi0=EIp/5 # scaling multiplier for the displacements esQkoormus(1,1:4,1)=[0.0 0.0 0.0 5.0]; esQkoormus(1,1:4,2)=[20.0 0.0 0.0 6.0]; esQkoormus(1,1:4,3)=[0.0 0.0 0.0 2.5];
# # Point load in local coordinate z and x directions kN # Fz, Fx, aF (coordinate of the point of force application) LoadsF_on_Element=5; esFjoud=zeros(LoadsF_on_Element,2,ElementideArv);
esFjoud(1,1:3,1)=[0.0 0.0 5.0]; esFjoud(1,1:3,2)=[0.0 0.0 6.0]; esFjoud(1,1:3,3)=[0.0 0.0 2.5];
# # Node forces in global coordinates # sSolmF(forces,1,nodes); forces=[Fx; Fz; My] sSolmF = zeros(3,1,SolmedeArv);
#sSolmF(:,1,1)= 0.0 sSolmF(2,1,1)= 800.0; % Fz sSolmF(1,1,2)= -90.0; % Fx sSolmF(2,1,2)= 800.0; % Fz #sSolmF(:,1,3)= 0.0 #sSolmF(:,1,4)= 0.0
# #s1F(1,1,1)=0.0; # force Fz #s1F(2,1,1)=0.0; # force Fz #s1F(3,1,1)=0.0; # force My # Support shift - tSiire# # Support shift is multiplied by scaling multiplier tSiire = zeros(3,1,SolmedeArv);
#tSiire(:,1,1)= 0.0 #tSiire(2,1,1)= 0.01*baasi0 #tSiire(:,1,2)= 0.0 #tSiire(:,1,3)= 0.0 #tSiire(:,1,4)= 0.0
#==========
# Nodal coordinates
#==========
krdn=[# x z
0.0 0.0; % node 1
6.0 0.0; % node 2
6.0 2.5; % node 3
0.0 5.0]; % node 4
#==========
#==========
# Restrictions on support displacements (on - 1, off - 0)
# Support No u w fi
#==========
tsolm=[3 1 1 0; % node 3
4 1 1 1]; % node 4
#==========
# ------------- Element properties, topology and hinges --------- elasts=[# Element properties # n2 - end of the element # n1 - beginning of the element # N, Q, M - hinges at the end of the element # N, Q, M - hinges at the beginning of the element # EIp EAp GAp 1 4 0 0 0 0 0 0; % element 1 EIr EAr GAr 2 1 0 0 0 0 0 0; % element 2 EIp EAp GAp 3 2 0 0 1 0 0 0]; % element 3 # 1 - hinge 'true' (axial, shear, moment hinges) #
2. Assembling and solving the boundary problem equations (6.5), carried out by the function Lahe2FrameDFIm(baasi0,Ntoerkts,esQkoormus,esFjoud,sSolmF,tsolm,tSiire, krdn,selem). The program has numbered the displacements and forces of the element ends of the frame as shown in Fig. 6.2.
The results of iteration of the axial forces are shown in excerpt 6.3 from the computing diary.
SIvec = Element Linear 1 2 3 4 5 1 -897.500 -904.385 -904.364 -904.364 -904.364 -904.364 2 -54.000 -55.431 -55.362 -55.362 -55.362 -55.362 3 -822.500 -815.615 -815.636 -815.636 -815.636 -815.636
The unscaled initial parameter vectors of the elements are shown in excerpt 6.4 from the computing diary.
-------- Scaling multiplier for displacements = 1/baasi0 -------- ============================================================================ Unscaled initial parameter vector Element No u w fi S H M ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 -0.000e+00 0.000e+00 0.000e+00 904.364 55.362 -154.733 2 -3.344e-02 2.261e-17 3.342e-04 55.362 -104.364 152.316 3 1.020e-17 3.344e-02 8.548e-03 815.636 34.638 -113.870 ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
The support reactions of the frame in global coordinates are shown in excerpt 6.5 from the computing diary.
Support reactions begin from X row: 37
===========================================
No X Node Cx <=> 1
Cz <=> 2
Cy <=> 3
-------------------------------------------
37 +3.463836e+01 3 1
38 -8.156356e+02 3 2
39 +5.536164e+01 4 1
40 -9.043644e+02 4 2
41 -1.547333e+02 4 3
--------------------------------------------
The bending moment, shear force Q and axial force N diagrams of the frame EST1 are shown in Fig. 6.3.
![\includegraphics[width=75mm]{joonised/raamnp4iIIe.eps}](img723.png) [Axial force N diagram] | ||
![\includegraphics[width=90mm]{joonised/raamnp3iIIe.eps}](img724.png) [Shear force Q diagram] |
![\includegraphics[width=68mm]{joonised/raamnp2iIIe.eps}](img725.png) [Bending moment diagram] | |
| (bracketed are values of linear solution) | ||
#================================================================================= Element displacements and forces determined by transfer matrix #================================================================================= Displacements and forces of element no 1 of length 5.000 m The element is divided into 4 parts displacement u - 0.00000e+00 -5.65228e-18 -1.13046e-17 -1.69568e-17 -2.26091e-17 displacement w - 0.00000e+00 -5.11088e-03 -1.65057e-02 -2.80093e-02 -3.34392e-02 rotation fi - 0.00000e+00 7.40749e-03 9.99497e-03 7.58070e-03 3.34242e-04 normal force N - -904.36438 -904.36438 -904.36438 -904.36438 -904.36438 shear force Q - -55.36164 -62.06071 -64.40074 -62.21735 -55.66392 moment force M - 154.73331 80.90916 1.40208 -78.20348 -152.31615 ------------------ axial force S - -904.36438 -904.36438 -904.36438 -904.36438 -904.36438 transv force H - -55.36164 -55.36164 -55.36164 -55.36164 -55.36164 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- Displacements and forces of element no 2 of length 6.000 m The element is divided into 4 parts displacement u - -3.34392e-02 -3.34392e-02 -3.34392e-02 -3.34392e-02 -3.34392e-02 displacement w - 2.26091e-17 3.39304e-03 8.42296e-03 8.39268e-03 3.29397e-10 rotation fi - 3.34242e-04 -3.73960e-03 -2.22252e-03 2.62995e-03 8.54847e-03 normal force N - -55.36164 -55.36164 -55.36164 -55.36164 -55.36164 shear force Q - 104.34587 74.57141 44.48742 14.21878 -16.10888 moment force M - -152.31615 -18.08174 71.24329 115.28819 113.87012 ------------------ axial force S - -55.36164 -55.36164 -55.36164 -55.36164 -55.36164 transv force H - 104.36438 74.36438 44.36438 14.36438 -15.63562 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- Displacements and forces of element no 3 of length 2.500 m The element is divided into 4 parts displacement u - 1.01954e-17 7.64658e-18 5.09772e-18 2.54886e-18 1.54074e-33 displacement w - 3.34392e-02 2.70705e-02 1.90043e-02 9.79115e-03 7.61059e-11 rotation fi - 8.54847e-03 1.16917e-02 1.39732e-02 1.53568e-02 1.58205e-02 normal force N - -815.63562 -815.63562 -815.63562 -815.63562 -815.63562 shear force Q - -41.61080 -44.17449 -46.03540 -47.16392 -47.54210 moment force M - 113.87012 87.02657 58.79850 29.63498 -0.00000 ------------------ axial force S - -815.63562 -815.63562 -815.63562 -815.63562 -815.63562 transv force H - -34.63836 -34.63836 -34.63836 -34.63836 -34.63836 ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Testing a static equilibrium for the frame
Consider next a static equilibrium of the frame shown in Fig. 6.4.
Let us project the forces onto the X-axis,