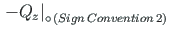Next: 5.3.2 Transfer matrix for Up: 5.3 Solutions of a Previous: 5.3 Solutions of a
 is
is
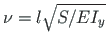 is a characteristic parameter of a beam-column member and
l is the length of the member.
is a characteristic parameter of a beam-column member and
l is the length of the member.
Consider next the Wronski determinant
 of the fundamental set of solutions from Eq. (5.37):
of the fundamental set of solutions from Eq. (5.37):
 value at
value at 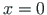 is not 1:
is not 1:
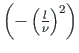
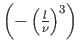
 .
.
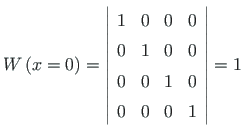 |
(5.41) |
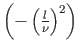 :
:
![$- \left(\frac{l}{\nu}\right)^{2}\left[\cos\left(\frac{\nu}{l}x\right) -
1\right]$](img572.png)
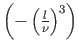 :
:
![$- \left(\frac{l}{\nu}\right)^{3}\left[\sin\left(\frac{\nu}{l}x\right) -
\left(\frac{\nu}{l}x\right)\right]$](img573.png)
 : x.
: x.
There are two sign conventions (see Fig. (1.2)) for the internal reactions 5.4 5.5 (contact forces).
For the parameters
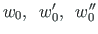 , and
, and
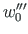 of the searchable function at
of the searchable function at 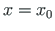 (Sign Convention 1) we obtain
(Sign Convention 1) we obtain
 =
=
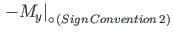
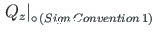 =
=