Next: C.2 Transfer matrices of Up: C. Transfer matrices Previous: C. Transfer matrices
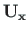 is the transfer matrix (Sign Convention 2):
is the transfer matrix (Sign Convention 2):
The loading vector
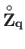 for a uniformly distributed load
for a uniformly distributed load 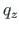 :
:
The loading vector
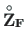 for a point load
for a point load 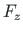 :
:
The transfer matrix 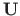 of the first-order analysis for a frame (Sign Convention 2)
can be computed using the GNU Octave function
ylfhlin.m
; for
a sparse transfer matrix U, the function ysplfhlin.m
is to be used.
of the first-order analysis for a frame (Sign Convention 2)
can be computed using the GNU Octave function
ylfhlin.m
; for
a sparse transfer matrix U, the function ysplfhlin.m
is to be used.
To compute the enlarged sparse transfer matrix
 of the first-order analysis
of the first-order analysis
The loading vectors in Tables C.1 and C.2 are comparable with those in [Krä91b] and [Bor79b].
The loading vectors
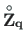 ,
,
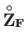 can be computed using the GNU Octave functions
yzhqz.m
and
yzfzv.m
.
can be computed using the GNU Octave functions
yzhqz.m
and
yzfzv.m
.
For a continuous beam, the loading vector
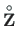 can be computed using the GNU Octave function ESTtalaKrmus.m
; to compute the vectors
can be computed using the GNU Octave function ESTtalaKrmus.m
; to compute the vectors
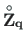 ,
,
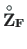 , the functions yzThqz.m
and yzTfzv.m
are used.
, the functions yzThqz.m
and yzTfzv.m
are used.
For a three-hinged frame, the loading vector
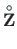 can be computed using the GNU Octave function ESTSKrmus.m
; to compute the vectors
can be computed using the GNU Octave function ESTSKrmus.m
; to compute the vectors
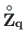 ,
,
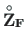 , the functions yzShqz.m
and yzSfzv.m
are used.
, the functions yzShqz.m
and yzSfzv.m
are used.
For a Gerber beam, the loading vector
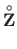 can be computed using the GNU Octave function ESTSTKrmus.m
; to compute the vectors
can be computed using the GNU Octave function ESTSTKrmus.m
; to compute the vectors
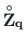 ,
,
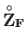 , the functions yzSThqz.m
and yzSTfzv.m
are used.
, the functions yzSThqz.m
and yzSTfzv.m
are used.
andres